Difference Between BSP and NPT Threads in Pipe Fittings
Index
• Global relevance of BSP and NPT standards
• What Are Pipe Threads?
• Overview of BSP Threads (BSPP, BSPT)
• Overview of NPT Threads (ANSI/ASME standard)
• Thread Geometry Comparison
• Key Differences Between BSP and NPT
• How to identify BSP and NPT threads?
• Can BSP and NPT Threads Be Used Together?
• Applications Across Regions
• Download Thread Chart

In the world of piping and fluid systems, threads are the unsung heroes. These spiral grooves carved into fittings and pipes may not grab attention like massive valves or shiny stainless-steel tanks, but they play one of the most critical roles: ensuring secure, leak-proof, and durable connections. Without the right thread, even the best-quality pipe fitting can fail.
Two of the most widely used standards globally are BSP (British Standard Pipe) and NPT (National Pipe Thread). At first glance, they look almost identical—so much so that many beginners assume they’re interchangeable. But in reality, they differ in geometry, standards, regions of use, and sealing mechanisms, which makes choosing the correct one essential for system safety and efficiency.
This blog will guide you through everything you need to know about BSP and NPT threads, including definitions, key differences, regional usage, and practical tips to avoid costly mistakes.
Why Pipe Threads Matter in Piping Systems
Before diving into BSP vs NPT, let’s take a step back. Why are threads so important?
Threads are essentially mechanical fasteners and sealing elements combined in one. They allow fittings to be assembled, disassembled, and reassembled with ease while maintaining leak-free performance. In industries such as oil and gas, water treatment, HVAC, chemical processing, and power generation, downtime caused by leaks or thread failure translates directly into lost money and safety hazards.
Choosing the wrong thread type might seem like a minor oversight, but it can lead to:
• Leaks under pressure → leading to safety risks or product contamination.
• Damage to fittings → cross-threading wears out components.
• System downtime → extra costs due to repairs or replacements.
• Failed inspections → especially in regulated industries.
This is why understanding BSP vs NPT is not just about technical curiosity—it’s about operational reliability.
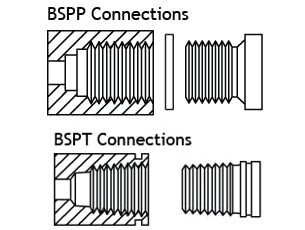
What is BSP (British Standard Pipe) Thread?
BSP, or British Standard Pipe thread, is the internationally recognized standard used widely in UK, Europe, Middle East, Asia, and Australia. It is governed by ISO standards and comes in two major forms:
1. BSPT (British Standard Pipe Tapered) – Defined by ISO 7-1, BSPT threads are tapered. This taper ensures that as the threads tighten, they wedge together to form a mechanical seal. BSPT fittings are commonly used in pressurized systems where a strong, reliable seal is required.
2. BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel) – Defined by ISO 228, BSPP threads are straight (parallel). Unlike BSPT, they cannot form a seal on their own and require a gasket, O-ring, or bonded washer to achieve leak-tightness. BSPP is popular in applications where frequent disassembly is expected, such as hydraulic systems.
A quick way to remember it?
• BSPT = Tapered = Seals on threads.
• BSPP = Parallel = Seals with gasket.
Industries using BSP threads: Plumbing, chemical plants, water treatment systems, food & beverage, and general industrial piping.
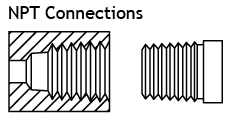
What is NPT (National Pipe Thread)?
On the other side of the globe, NPT is the standard used primarily in USA, Canada, and North America. Defined by ASME B1.20.1, NPT threads are always tapered.
That taper—typically at 1°47′—allows the male and female threads to wedge tightly as they are screwed together. The tighter they’re turned, the more the threads bind. This provides a mechanical seal, but to ensure complete leak-proof performance, installers usually add PTFE tape (commonly called Teflon tape) or thread sealant.
Industries using NPT threads: Oil & gas, HVAC, fire protection systems, petrochemical, power generation, and water treatment.
BSP vs NPT Threads – Key Differences
Although BSP and NPT look quite similar at first glance, there are critical differences that make them non-interchangeable. Here’s a technical breakdown:
| Feature | BSP (BSPT / BSPP) | NPT (National Pipe Thread) |
|---|---|---|
| Governing Standard | ISO 7/1 (BSPT), ISO 228 (BSPP) | ASME B1.20.1 |
| Thread Angle | 55° | 60° |
| Crest & Root Shape | Rounded | Flattened |
| Types Available | Tapered (BSPT) & Parallel (BSPP) | Tapered only |
| Seal Mechanism | BSPT seals on threads, BSPP requires gasket/O-ring | Seals on threads + sealant (PTFE tape) |
| Common Regions | UK, EU, Middle East, Asia, Australia | USA, Canada, North America |
How to identify BSP and NPT Threads in practice?
In simpler terms:
• BSP threads are a little rounder (55°), while NPT threads are sharper (60°).
• BSP comes in both parallel and tapered versions, while NPT is always tapered.
• BSP connections often rely on an O-ring or washer for sealing, while NPT relies heavily on thread engagement and sealant.
Can BSP and NPT Threads Be Used Together?
Here’s a question many engineers and procurement managers ask: Can I connect a BSP fitting to an NPT fitting?
The short answer: No, not reliably.
Why?
• The angles don’t match (55° vs 60°).
• The pitch is slightly different.
• The crest and root geometry doesn’t align.
Sure, in some cases, you may physically screw them together and think they fit, but under pressure, they’ll almost always leak. Worse, the improper fit may damage the threads, making the fittings unusable.
The only safe way to mix BSP and NPT systems is by using precision adapters designed specifically for BSP–NPT conversion.
Regional Usage – Where Each Standard Rules
Understanding where BSP and NPT dominate helps avoid procurement confusion:
• USA & Canada → NPT is standard across industries.
• UK & EU → BSP threads are the norm.
• Middle East → Both BSP and NPT are found, depending on the project specification.
• Australia → BSP is more common, though NPT is also used for imported systems.
BSP vs NPT – Which One Should You Choose?
Choosing between BSP and NPT isn’t about personal preference—it’s about compliance and compatibility.
• If your project is in North America, you’ll almost certainly need NPT.
• If it’s in Europe, the Middle East, or Australia, BSP is the safer bet.
• For global projects, don’t assume one will work everywhere—always check the project specification documents.
One practical tip: We often maintain stock of both BSP and NPT fittings, along with adapters, to cover international requirements without delays.
Practical Tips for Engineers and Buyers
1. Double-check specifications before ordering—especially in international projects.
2. Avoid mixing BSP and NPT unless you have a certified adapter.
3. Use sealants properly—PTFE tape for NPT, O-rings or gaskets for BSPP.
4. Train installation teams to recognize thread types visually (pitch gauges help too).
5. Work with suppliers who clearly specify thread standards in product datasheets.
Conclusion
BSP and NPT threads may look similar, but in practice, they’re worlds apart. Using the wrong one can mean leaks, costly downtime, and failed inspections. The key differences—thread angle, sealing method, and region of dominance—should always guide your decision.
Think of it this way: BSP and NPT are like two different languages. Both get the job done in their own regions, but they aren’t interchangeable. Understanding which one to use (and when) will save you frustration, time, and money.
So, the next time you’re sourcing pipe fittings, ask the simple but critical question: BSP or NPT? That one detail might just be the difference between a leak-free system and a maintenance nightmare.
At C-Way Engineering Exports, we manufacture and supply high-quality steel pipe fittings with BSP and NPT threading, designed for leak-free and durable performance across industries. Whether your project is in the USA, Canada, UK, EU, UAE, Middle East, or Australia, we provide precision-engineered fittings tailored to international standards.
Contact us today for reliable pipe fittings that ensure perfect compatibility and long-term performance in your applications.






