When it comes to connecting pipes in industrial systems, flanges are like the “handshakes” of the pipeline world — they bring two ends together, make a secure connection, and if needed, allow you to part ways just as easily.
But here’s the thing — in Europe, not all handshakes are the same. DIN and EN standard flanges follow specific rules that ensure compatibility, safety, and long-term performance across industries.
If you’ve ever worked on a European industrial project — whether it’s in oil & gas, chemical processing, water treatment, or power generation — you know flanges aren’t just “pipe connectors.” They’re the unsung heroes of every piping system, keeping fluids where they’re supposed to be, ensuring safe operations, and making maintenance possible without tearing the whole line apart.
In Europe, DIN (Deutsches Institut für Normung) and EN (European Norm) standards are the gold standard for flange manufacturing and selection. But here’s the thing: not all flanges are created equal, and choosing the wrong one can lead to expensive downtime, safety hazards, or even project delays.
So, let’s roll up our sleeves and dive deep into what makes DIN and EN flanges the go-to choice for European industries — from types and materials to dimensions and applications.
1. What Makes DIN and EN Standards Special?
Think of DIN and EN standards as the grammar of industrial piping. Just as grammar keeps a sentence understandable, these standards make sure every flange fits, performs, and lasts as expected — no matter where in Europe you source or install it.
• DIN Standards – Developed in Germany but widely adopted across Europe for decades, these specify exact measurements, pressure ratings, and tolerances.
• EN Standards – Introduced to harmonize European technical specifications, often aligning with international ISO standards but retaining the precision Europe is known for.
Both ensure interchangeability (a flange from Italy fits with one from Germany) and guarantee performance under specified conditions.
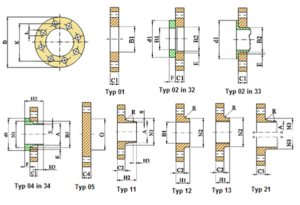
2. Types of DIN and EN Flanges (and When to Use Them)
The type of flange you choose depends on your pipeline’s pressure, temperature, fluid type, and maintenance needs. Let’s break down the most common ones:
a. Weld Neck Flange (DIN 2631–2638 / EN 1092-1 Type 11)
• Best for: High pressure, high temperature, cyclic loading
• Key feature: Long tapered hub for stress distribution, butt-welded for leak-free performance
• Typical sizes: DN 10 to DN 2000
• Pressure ratings: PN 6 to PN 400
b. Slip-On Flange (DIN 2573–2576 / EN 1092-1 Type 12)
• Best for: Low to medium pressure systems, easier installation
• Key feature: Slides over the pipe, fillet welded on both sides
• Pressure ratings: PN 6 to PN 40
c. Blind Flange (DIN 2527 / EN 1092-1 Type 05)
• Best for: Closing pipeline ends or vessel nozzles
• Key feature: Solid disk, allows pressure testing or future expansion
• Pressure ratings: PN 6 to PN 400
d. Threaded Flange (DIN 2565–2566 / EN 1092-1 Type 13)
• Best for: Systems where welding isn’t possible (flammable fluids, field installation)
• Key feature: Female thread matches pipe’s male thread
e. Lap Joint Flange (DIN 2641–2642 / EN 1092-1 Type 02)
• Best for: Systems requiring frequent dismantling
• Key feature: Works with a stub end, minimal stress on the flange
f. Socket Weld Flange (DIN 2629 / EN 1092-1 Type 14)
• Best for: Small bore, high pressure lines
• Key feature: Socket for pipe insertion, fillet welded for strength
3. Materials: Matching the Right Alloy to the Job
Choosing the wrong material for your flange is like wearing flip-flops to a mountain hike — you’ll regret it fast. Material choice is driven by fluid type, temperature, pressure, and corrosion resistance requirements.
Common Materials for DIN & EN Flanges
• Carbon Steel – Cost-effective, ideal for water, steam, and oil (e.g., C22.8, P245GH)
• Stainless Steel – Excellent corrosion resistance for chemical, food, and pharma (e.g., 1.4301 / AISI 304, 1.4404 / AISI 316L)
• Duplex Stainless Steel – Higher strength and chloride resistance for seawater systems
• Alloy Steels – For high-temperature service (e.g., 16Mo3, 13CrMo4-5)
• Copper-Nickel Alloys – Marine and desalination applications
• Ductile Iron – Cost-efficient for low-pressure water lines
4. Dimensions and Pressure Ratings: The Technical Backbone
DIN & EN flanges are specified by:
• Nominal Diameter (DN) – e.g., DN 50 = 50 mm
• Pressure Nominal (PN) – PN 6, PN 10, PN 16, PN 25, PN 40, PN 63, PN 100, PN 160, PN 250, PN 400
• Facing Type – Raised Face (RF), Flat Face (FF), Ring Type Joint (RTJ)
• Bolt Hole Circle Diameter (BCD) and Number of Holes – Critical for interchangeability
DIN EN 1092-1 Flange Table (DN10–DN600, PN6–PN40)
| DN | PN | OD D (mm) | Bolt Circle (K) | Bolt Qty / Dia. | Raised Face Dia. d4 (mm) | Hub Dia. (Weld Neck) (mm) | Flange Thickness C (mm) | Approx. Weight (kg) | Gasket Face Finish (Ra µm) | Bolt Torque (Nm, Grade 8.8) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 6 | 90 | 60 | 4 × M12 | 40 | 22 | 14 | 0.6 | 3.2–6.3 | 25 |
| 10 | 10 | 90 | 60 | 4 × M12 | 40 | 22 | 16 | 0.7 | 3.2–6.3 | 30 |
| 10 | 16 | 90 | 60 | 4 × M12 | 40 | 22 | 18 | 0.8 | 3.2–6.3 | 35 |
| 10 | 25 | 90 | 60 | 4 × M12 | 40 | 22 | 20 | 0.9 | 3.2–6.3 | 40 |
| 10 | 40 | 100 | 60 | 4 × M14 | 45 | 22 | 22 | 1.1 | 3.2–6.3 | 55 |
| 25 | 6 | 115 | 85 | 4 × M12 | 68 | 38 | 16 | 1.4 | 3.2–6.3 | 35 |
| 25 | 10 | 115 | 85 | 4 × M12 | 68 | 38 | 18 | 1.6 | 3.2–6.3 | 40 |
| 25 | 16 | 115 | 85 | 4 × M12 | 68 | 38 | 20 | 1.8 | 3.2–6.3 | 45 |
| 25 | 25 | 125 | 85 | 4 × M14 | 72 | 38 | 22 | 2.0 | 3.2–6.3 | 55 |
| 25 | 40 | 140 | 100 | 4 × M16 | 80 | 38 | 26 | 2.5 | 3.2–6.3 | 75 |
| 50 | 6 | 165 | 125 | 4 × M16 | 102 | 60 | 18 | 3.0 | 3.2–6.3 | 75 |
| 50 | 10 | 165 | 125 | 4 × M16 | 102 | 60 | 20 | 3.3 | 3.2–6.3 | 80 |
| 50 | 16 | 165 | 125 | 4 × M16 | 102 | 60 | 22 | 3.6 | 3.2–6.3 | 90 |
| 50 | 25 | 175 | 125 | 4 × M16 | 105 | 60 | 24 | 4.0 | 3.2–6.3 | 100 |
| 50 | 40 | 190 | 145 | 4 × M20 | 115 | 60 | 28 | 5.2 | 3.2–6.3 | 160 |
| 100 | 6 | 220 | 180 | 8 × M16 | 158 | 114 | 20 | 6.8 | 3.2–6.3 | 80 |
| 100 | 10 | 220 | 180 | 8 × M16 | 158 | 114 | 22 | 7.5 | 3.2–6.3 | 90 |
| 100 | 16 | 220 | 180 | 8 × M16 | 158 | 114 | 24 | 8.2 | 3.2–6.3 | 100 |
| 100 | 25 | 235 | 190 | 8 × M20 | 165 | 114 | 26 | 9.4 | 3.2–6.3 | 160 |
| 100 | 40 | 265 | 210 | 8 × M24 | 185 | 114 | 30 | 12.5 | 3.2–6.3 | 250 |
| 300 | 6 | 445 | 400 | 12 × M20 | 365 | 273 | 26 | 30.0 | 3.2–6.3 | 160 |
| 300 | 10 | 445 | 400 | 12 × M20 | 365 | 273 | 28 | 33.0 | 3.2–6.3 | 180 |
| 300 | 16 | 445 | 410 | 12 × M22 | 375 | 273 | 30 | 35.0 | 3.2–6.3 | 210 |
| 300 | 25 | 460 | 430 | 16 × M24 | 390 | 273 | 34 | 42.0 | 3.2–6.3 | 260 |
| 300 | 40 | 515 | 460 | 16 × M27 | 420 | 273 | 38 | 52.0 | 3.2–6.3 | 320 |
| 600 | 6 | 770 | 695 | 20 × M27 | 675 | 610 | 32 | 98.0 | 3.2–6.3 | 320 |
| 600 | 10 | 770 | 695 | 20 × M27 | 675 | 610 | 36 | 110.0 | 3.2–6.3 | 360 |
| 600 | 16 | 780 | 705 | 20 × M30 | 685 | 610 | 40 | 125.0 | 3.2–6.3 | 420 |
| 600 | 25 | 840 | 755 | 24 × M30 | 735 | 610 | 44 | 145.0 | 3.2–6.3 | 460 |
| 600 | 40 | 940 | 840 | 24 × M36 | 820 | 610 | 50 | 180.0 | 3.2–6.3 | 650 |
How to Use This Table
1. Select DN & PN: Choose nominal bore and pressure class based on your pipeline design.
2. Check Bolt Torque: Apply the recommended torque as a baseline; adjust per gasket type.
3. Verify Raised Face Finish: Match gasket face finish to gasket material to avoid leaks.
4. Confirm Hub Dimensions: Particularly for weld neck flanges, to ensure pipe-wall compatibility.
5. Review Weight: For handling, shipping, and support calculations.
NOTE
Blind Flanges (Type 05)
• Thickness is generally greater than plate or weld neck flanges for the same PN.
• Weight is ~10–15% higher due to the solid face.
• Bolt torque values remain the same, as they depend on bolt size and gasket.
5. Manufacturing & Quality Control
A flange isn’t just cut from steel and shipped. High-quality European flanges follow rigorous manufacturing steps:
1. Material Inspection – Verify chemical composition (EN 10204 3.1 / 3.2 certificates)
2. Forging / Casting – Forging preferred for strength, casting for complex shapes
3. Machining – CNC turning for precise sealing faces and bolt hole alignment
4. Heat Treatment – Stress relieving for dimensional stability
5. Surface Finish – Ra value critical for gasket sealing (typically 3.2–6.3 μm for RF)
6. Testing – Dimensional checks, PMI (Positive Material Identification), pressure testing if required
6. Applications Across European Industries
DIN & EN flanges aren’t one-size-fits-all; their application is dictated by the industry’s working environment:
• Oil & Gas – Weld neck flanges for high-pressure, high-temp offshore and onshore pipelines
• Chemical Processing – Stainless steel EN 1092-1 flanges for aggressive acids and solvents
• Water Treatment – Ductile iron PN 16 slip-on flanges for municipal pipelines
• Food & Beverage – Hygienic stainless steel flanges with smooth finishes for CIP systems
• Power Generation – Alloy steel flanges for steam lines up to 600°C
• Marine & Offshore – Copper-nickel flanges for seawater cooling systems
7. Why Compliance and Certification Matter
In Europe, compliance isn’t just a box to tick — it’s a legal and safety requirement.
Look for flanges certified to:
• EN 1092-1 dimensional standards
• PED 2014/68/EU Pressure Equipment Directive compliance
• ISO 9001:2015 quality management
• CE Marking for regulatory conformity
• EN 10204 3.1 / 3.2 inspection certificates
8. The Bottom Line: Why DIN & EN Flanges Are the Smart Choice
Whether you’re engineering a petrochemical plant in Germany, upgrading a water network in France, or building a food processing facility in Italy, DIN & EN flanges give you the peace of mind that everything will fit, perform, and last.
Investing in high-quality, certified flanges is not just about passing inspections — it’s about long-term reliability, reduced maintenance, and keeping your operations running smoothly.
When it comes to sourcing high-quality DIN and EN standard flanges for European industries, precision, compliance, and reliability matter most—and that’s exactly what we deliver at C-Way Engineering Exports. With decades of manufacturing expertise, ISO 9001:2015 certification, CE compliance, and strict adherence to DIN, EN, ASTM, and ANSI standards, we engineer flanges that perform flawlessly under the toughest operating conditions. Whether you need carbon steel, stainless steel, Duplex & Super duplex or special alloy flanges, customized dimensions, or urgent delivery for your EPC projects, our team is ready to support you from inquiry to installation. Let’s work together to make your next project a success—contact us today for a technical consultation or a competitive quote.
If you are working on projects that require strict adherence to European specifications, our DIN standard valves offer the perfect balance of precision, durability, and compliance. From DIN ball valves to DIN butterfly valves, we manufacture solutions that meet EN, DIN, and PED requirements for seamless integration into European pipelines.