ASME B16.5 Flanges Explained: Types, Dimensions, and Pressure Ratings for Industrial Piping Systems
In industrial piping systems, the reliability of connections determines the long-term safety and efficiency of the entire network. Among the most widely recognized flange standards globally, ASME B16.5 defines the design, dimensions, materials, and pressure ratings of
pipe flanges and flanged fittings up to 24 inches nominal pipe size (NPS).
Whether used in oil & gas, petrochemical, power generation, water treatment, or marine industries, ASME B16.5 flanges are critical for ensuring leak-proof joints under demanding pressure and temperature conditions.
This comprehensive guide explains the types, dimensions, pressure ratings, and material grades defined under the ASME B16.5 standard, helping engineers and procurement professionals make the right selection for their piping systems.
What is ASME B16.5?
ASME B16.5 is a standard developed by the
American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME).
It specifies the dimensions, tolerances, materials, pressure-temperature ratings, and testing requirements for flanges and flanged fittings used in piping systems.
The standard covers:
- Nominal Pipe Sizes (NPS): ½” to 24″
- Pressure Classes: 150, 300, 400, 600, 900, 1500, and 2500
- Flange Facing Types: Raised Face (RF), Flat Face (FF), and Ring-Type Joint (RTJ)
ASME B16.5 is often referred to interchangeably with ANSI B16.5, as it was originally published under the ANSI (American National Standards Institute) designation before being adopted by ASME.
This standard ensures global uniformity, enabling manufacturers, EPC contractors, and maintenance engineers to design and assemble piping systems with complete compatibility across different suppliers and equipment.
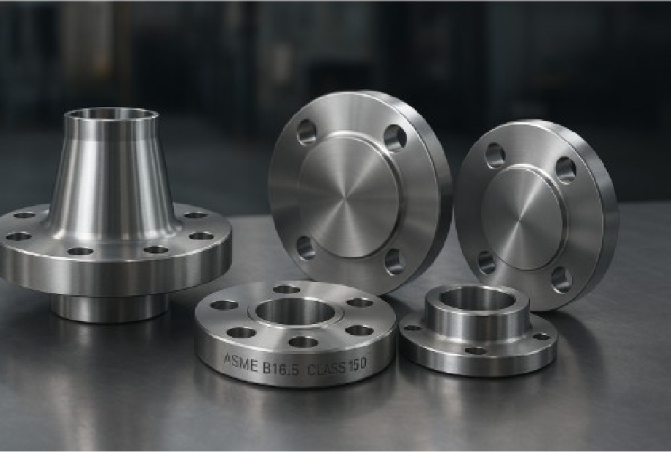
Flange Types Covered Under ASME B16.5
ASME B16.5 classifies several flange types based on how they connect to pipes and their intended service conditions.
Each serves a specific mechanical and operational purpose, ensuring reliable and leak-proof connections in industrial piping systems.


| Flange Type | Description | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Weld Neck Flange (WN) | Features a long tapered hub for excellent stress distribution; butt-welded to the pipe neck. | High-pressure, high-temperature services such as steam and oil & gas pipelines. |
| Slip On Flange (SO) | Slides over the pipe and is fillet-welded on both sides. | Low-pressure applications; easy to align and install. |
| Blind Flange (BL) | Has no bore; used to seal or close the end of a piping system. | Pipeline isolation, hydro testing, or maintenance closures. |
| Socket Weld Flange (SW) | Pipe is inserted into a socket and fillet-welded around the hub. | Small-bore, high-pressure lines like hydraulic or steam systems. |
| Threaded Flange (TH) | Internal threads allow the flange to be screwed directly onto externally threaded pipes. | Used in systems where welding is not possible, such as explosive or flammable environments. |
| Lap Joint Flange (LJ) | Used with a stub end; the flange can rotate freely around the pipe. | Ideal for systems requiring frequent dismantling, cleaning, or inspection, especially in corrosive services. |
| Orifice Flange | Similar to weld neck or slip-on flanges but with a precision-machined hole for flow measurement. | Used with orifice plates, flow nozzles, and differential pressure transmitters in metering systems. |
| Reducing Flange | Has differing bore sizes on each side to connect pipes of different diameters. | Compact alternative to using separate reducers in tight piping layouts. |
| Expander Flange | Used to increase pipe size at the flange connection. | Ideal for connecting pumps, compressors, or valves to larger diameter pipelines. |
| Weld Ring Hub Flange | Consists of a hub welded to the pipe and a loose backing flange. | Common in high-pressure, high-cycle systems requiring uniform load distribution. |
| Flat Flange (FF) | Provides a flat sealing face and is used with full-face gaskets. | Suitable for cast iron or fiberglass piping systems. |
| Ring-Type Joint Flange (RTJ) | Has a machined groove for metallic ring gaskets that provide a metal-to-metal seal. | Used in high-pressure, high-temperature, and critical sealing applications. |
Dimensional Standards and Pressure Ratings
1. Dimensional Ranges
ASME B16.5 defines precise dimensions for:
- Outside Diameter (OD)
- Bolt Circle Diameter (BCD)
- Number and size of bolts
- Hub height
- Flange thickness
- Raised face height
For example, a 6-inch Class 150 Weld Neck Flange will have standard dimensions recognized across all manufacturers — ensuring full interchangeability worldwide.
2. Pressure-Temperature Ratings
Precision-engineered ASME B16.5 flanges manufactured by C-Way Engineering Exports for global industrial applications
| Pressure Class | Approx. Working Pressure (at 38°C / 100°F) |
|---|---|
| Class 150 | Up to 19.6 bar (285 psi) |
| Class 300 | Up to 51 bar (740 psi) |
| Class 600 | Up to 103 bar (1480 psi) |
| Class 900 | Up to 155 bar (2220 psi) |
| Class 1500 | Up to 258 bar (3705 psi) |
| Class 2500 | Up to 430 bar (6205 psi) |
These ratings vary with material grade — stainless steel flanges can withstand higher temperatures compared to carbon steel before derating occurs.
Materials and Grade Options for ASME B16.5 Flanges
ASME B16.5 flanges are available in a wide range of materials to meet diverse industrial needs. Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance, while carbon steel provides strength and economy for general industrial use. Alloy steel is ideal for high-temperature service, and duplex/super duplex ensures superior strength in corrosive environments. For specialized applications, nickel alloys (Inconel, Monel, Hastelloy), copper-nickel and bronze or ductile iron options are also available, ensuring reliable performance across various piping systems.
ASME B16.5 flanges can be manufactured from a wide range of metallic materials depending on service temperature, pressure class, and fluid characteristics. The most commonly used materials are as follows:
1. Stainless Steel Flanges
Used for corrosive and high-temperature environments such as chemical, food, water treatment, and offshore industries.
- Common Grades:
- ASTM A182 F304 / F304L
- ASTM A182 F316 / F316L
- ASTM A182 F321 / F347
- ASTM A182 F310 / F317
- ASTM A182 F904L (Super Austenitic Stainless Steel)
- Key Benefits:
- Excellent corrosion and oxidation resistance
- Suitable for both cryogenic and elevated temperatures
- Long service life in chemical and marine environments
2. Carbon Steel Flanges
Most widely used for general-purpose applications such as oil & gas, petrochemical, and power generation.
- Grades:
- ASTM A105 – Forged carbon steel for ambient temperature service
- ASTM A350 LF2 – Low-temperature carbon steel for cryogenic applications
- ASTM A694 F42, F46, F52, F60, F65, F70 – High-yield carbon steel for high-pressure services
- Key Benefits:
- High tensile strength and toughness
- Cost-effective for standard industrial pipelines
- Easy to weld and machine
3. Alloy Steel Flanges
Designed for higher strength and temperature resistance compared to carbon steel. Commonly used in power plants, refineries, and high-temperature chemical processing.
- Grades:
- ASTM A182 F1, F5, F9, F11, F12, F22, F91
- ASTM A182 F91 (Cr-Mo-V Steel) for high-temperature, high-pressure steam lines
- Key Benefits:
- Superior strength under high pressure and thermal stress
- Excellent resistance to creep, oxidation, and scaling
4. Duplex & Super Duplex Flanges
Provide an exceptional combination of strength and corrosion resistance, especially against chloride-induced stress corrosion cracking.
- Grades:
- ASTM A182 F51 (UNS S31803) – Duplex
- ASTM A182 F53 (UNS S32750) – Super Duplex
- ASTM A182 F55 (UNS S32760) – Super Duplex
- Key Benefits:
- Twice the strength of standard stainless steel
- Excellent performance in seawater and brine environments
- Common in offshore and desalination applications
5. Nickel Alloy Flanges
Used in extremely corrosive environments such as acid production, chemical processing, and marine industries.
- Grades:
- ASTM B564 N04400 (Monel 400)
- ASTM B564 N06600 / N06625 (Inconel 600 / 625)
- ASTM B564 N08800 / N08825 (Incoloy 800 / 825)
- ASTM B564 N10276 (Hastelloy C276)
- Key Benefits:
- Excellent resistance to acids (hydrochloric, sulfuric, phosphoric)
- High mechanical strength at elevated temperatures
6. Copper Nickel Flanges
Preferred for seawater, shipbuilding, and desalination plant applications due to excellent biofouling resistance.
- Grades:
- ASTM B151 C70600 (90/10 Cu-Ni)
- ASTM B151 C71500 (70/30 Cu-Ni)
- Key Benefits:
- Excellent resistance to seawater corrosion and marine organisms
- Commonly used in marine piping, condensers, and heat exchangers
7. Titanium & Special Alloys
Used in highly corrosive or high-performance environments such as chemical plants, aerospace, and offshore oil production.
- Grades:
- ASTM B381 Gr.2, Gr.5 (Titanium)
- ASTM B564 N06625 (Inconel 625)
- ASTM B564 N08825 (Incoloy 825)
- Key Benefits:
- Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio
- Outstanding resistance to acid corrosion and oxidation
C-Way Engineering Exports manufactures ASME B16.5 flanges in all these material grades to meet diverse industrial requirements.
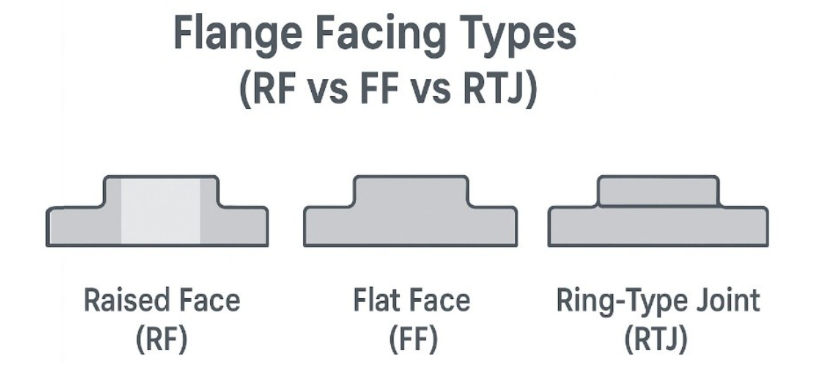
Facing Types in ASME B16.5 Flanges
| Facing Type | Description | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Raised Face (RF) | Most common; a small raised area where the gasket is seated. | General industrial piping. |
| Flat Face (FF) | Flat gasket contact surface. | Cast iron or fiberglass flanges. |
| Ring-Type Joint (RTJ) | Uses a metal ring gasket in a groove. | High-pressure and high-temperature systems. |
Selecting the right flange facing ensures proper sealing and longevity of the joint.
Applications of ASME B16.5 Flanges
- Oil & Gas: Upstream and downstream pipeline networks.
- Petrochemical: For handling corrosive and high-pressure fluids.
- Power Generation: Used in boiler lines, condensate, and steam piping.
- Water Treatment: Stainless steel flanges for corrosion resistance in filtration systems.
- Marine & Offshore: Carbon and stainless steel flanges for seawater lines and ballast systems.
- Mining: For slurry transport, process water, and compressed air systems.
Each application demands precise flange selection based on pressure class, temperature, corrosion resistance, and maintenance requirements.
Comparison: ASME B16.5 vs ASME B16.47
While ASME B16.5 covers flanges up to 24 inches (NPS 24), the ASME B16.47 standard applies to larger diameter flanges (NPS 26 to NPS 60).
| Parameter | ASME B16.5 | ASME B16.47 |
|---|---|---|
| Size Range | NPS ½ – 24 | NPS 26 – 60 |
| Pressure Classes | 150 – 2500 | 75 – 900 |
| Application | Standard piping | Large-diameter pipelines |
| Series | Single standard | Series A & Series B
|
For large-diameter process pipelines, engineers refer to ASME B16.47, while for regular process lines, ASME B16.5 remains the standard choice.
Conclusion
ASME B16.5 flanges are the backbone of reliable industrial piping systems, ensuring secure, standardized, and leak-free connections across industries. Understanding the correct flange type, pressure class, and material is critical for long-term system integrity.
As a trusted global manufacturer and exporter of industrial valves, pipe fittings and flanges,
C-Way Engineering Exports offers precision-engineered ASME B16.5 stainless steel, carbon steel, and alloy steel flanges conforming to the highest quality and dimensional accuracy.
Looking for reliable ASME B16.5 flanges for your next project?
Contact C-Way Engineering Exports — your trusted global partner for high-performance flanges built to ASME, ANSI, DIN, and EN standards.
We deliver precision, quality, and global compliance in every connection.
FAQs
Q1: Are ASME B16.5 flanges compatible with EN or DIN flanges?
A: Not directly; dimensions and bolt patterns differ. Adaptors or matched pairs are required for mixed-standard systems.
Q2: How do I identify flange pressure class?
A: It’s typically stamped on the flange face or rim (e.g., CL150, CL300, CL600).
Q3: What gasket materials are suitable for ASME B16.5 flanges?
A: For RF — non-metallic gaskets (spiral wound, PTFE, graphite). For RTJ — metallic ring-type gaskets (R, RX, BX types).
Q4: Do surface finishes affect sealing performance?
A: Yes. ASME B16.5 specifies surface finish roughness between 125–500 µinches for optimal gasket seating.





